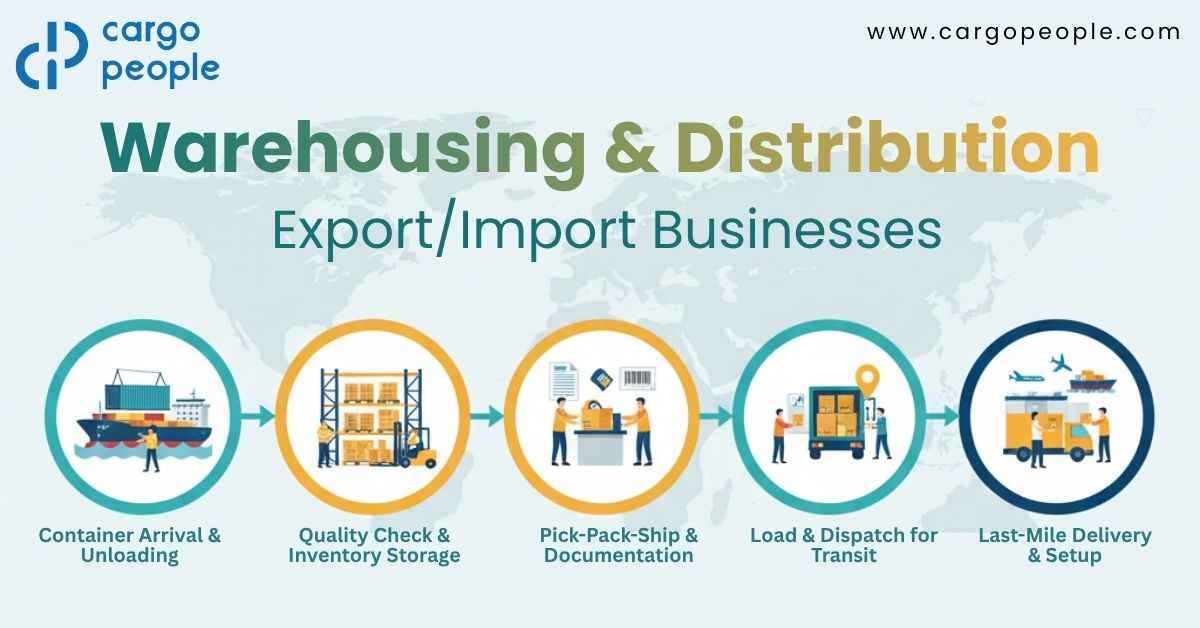
Introduction — The Story Behind Every On-Time Shipment
When Delta Exports Pvt. Ltd., an auto component manufacturer from Pune, lost a ₹12 lakh shipment due to delays in port consolidation, the issue wasn’t the freight—it was poor warehouse coordination.
Their cargo sat idle for four days at Nhava Sheva because of incomplete customs documentation and delayed truck scheduling. Once they shifted to a bonded warehousing model near the port, clearance time dropped by 40% and their German buyers got deliveries on schedule again.
This is a familiar story for many Indian exporters. In international trade, efficient warehousing and distribution aren’t optional—they’re the difference between missed deadlines and market leadership.
The Strategic Role of Warehousing in India’s Export-Import Supply Chain
In India’s growing logistics ecosystem, warehousing has evolved from a storage function into a strategic trade enabler. Modern warehouses do more than stock goods—they optimize duty payments, streamline customs clearance, and connect multi-modal transport networks.
Why warehousing matters to exporters and importers:
-
Duty deferment: Goods can stay in bonded storage without paying customs duty upfront, improving cash flow.
-
Faster consolidation: Shipments from multiple suppliers can be merged before export, reducing freight cost per CBM.
-
Reduced demurrage: Efficient warehouse coordination minimizes port dwell time and container detention.
-
Compliance readiness: Adherence to WDRA, DGFT, and Customs Act standards reduces regulatory risk.
Industry Insight:
As per India’s National Logistics Policy, improved warehouse infrastructure could reduce logistics costs from 14% to below 10% of GDP—a direct saving for export-oriented businesses.
Types of Warehousing Facilities in India for Export/Import Businesses
Bonded Warehouses: Managing Costs and Compliance
A bonded warehouse allows importers to store goods without paying customs duty until the items are released for sale or re-export. This flexibility helps businesses manage cash flow and avoid immediate taxation.
Key requirements:
-
License under Section 58 of the Customs Act.
-
Security bond or bank guarantee equal to duty payable.
-
Warehouse registration and record maintenance through the ICEGATE module (2024 update).
Business Use Case:
An electronics importer stores components in a bonded facility near Mumbai and releases them gradually to the domestic market. This way, the company avoids paying duties on entire shipments at once and optimizes working capital.
Free Trade Warehousing Zones (FTWZs): A Global Trade Advantage
FTWZs, governed under the SEZ Act, function as international trade hubs for storage, consolidation, and value-added operations. They are particularly useful for re-exporters and global trading houses managing multi-country flows.
Advantages for exporters/importers:
-
Goods can be stored duty-free indefinitely.
-
Ideal for labeling, repackaging, and light assembly.
-
No GST until goods move into the Domestic Tariff Area (DTA).
-
International buyers can buy and sell goods within FTWZs without physical export.
Example:
A pharma exporter in Ahmedabad ships to an FTWZ in Chennai, repacks under cold-chain control, and re-exports to Singapore—saving nearly ₹4 lakh per consignment in deferred tax and reduced freight cost.
Private and Public Distribution Centers
Distribution centers (DCs) are the link between warehouses and transport corridors. Many exporters now rely on integrated 3PL distribution solutions to improve responsiveness and reduce handling costs.
Core features:
-
RFID-based tracking and WMS integration.
-
Controlled environments for perishables and pharma.
-
Consolidation and cross-docking for time-sensitive cargo.
-
Multi-location delivery network for import distribution.
Practical insight:
By outsourcing distribution logistics, a textile exporter in Tirupur achieved a 35% reduction in order turnaround time, as the 3PL provider handled both port delivery and customer dispatches.
India’s Warehousing Market Snapshot (2025)
| Metric | FY24–25 Estimate | Implication for Exporters/Importers |
|---|---|---|
| Warehousing Market Size | USD 25 Billion | Rapid expansion driven by EXIM & e-commerce growth |
| Share of Grade A Facilities | 42% | Reflects rise in organized, compliant warehouses |
| Key Port-Based Clusters | Nhava Sheva, Mundra, Chennai, Kolkata | Handle 68% of India’s EXIM warehousing volume |
| Investment Growth (YoY) | +203% (2024–25) | Huge opportunity for cost-effective 3PL partnerships |
Interpretation:
Indian warehousing is shifting towards digital, compliant, and port-adjacent operations. For exporters, that means better inventory visibility and faster cross-border trade cycles.
Distribution Logistics: The Link Between Warehouse and Global Buyer
Efficient distribution logistics is about connecting goods from warehouses to ports, airports, or customers with minimal delays. Poor coordination can lead to demurrage costs, missed sailing schedules, and shipment rollover—issues that directly affect profitability.
Strategies to enhance distribution efficiency:
-
Hub-and-Spoke Models: Use a central hub (Delhi NCR or Mumbai) connected to smaller spokes for regional dispatch.
-
Multi-Modal Connectivity: Integrate rail, road, and coastal shipping for faster delivery.
-
Data-Driven Planning: Forecast port congestion and align dispatch schedules.
-
Inventory Buffering: Maintain minimal stock near ports like Mundra and JNPT to handle last-minute orders.
Industry Perspective:
Leading 3PLs now use AI-driven visibility tools integrated with ULIP and LDB systems, helping exporters predict transit delays and reroute in real-time.
Compliance & Operational Risks to Avoid
Customs compliance errors remain a major risk area for importers. In 2024, several companies faced penalties for failing to file monthly bonded warehouse returns through the new ICEGATE module.
| Regulation / Authority | Requirement |
|---|---|
| CBIC (Circular 19/2024) | Online licensing and bond-to-bond transfer via ICEGATE |
| WDRA | Periodic warehouse registration, safety audits, and storage standards |
| DGFT | Export obligation tracking under EPCG/Advance Authorization |
| BIS/FSSAI | Product quality and labeling compliance for imports |
| Customs Act 1962 | Accurate declaration and documentation of goods |
Real-World Example:
An electronics importer in Noida incurred ₹7.5 lakh in demurrage for delayed documentation updates under the ICEGATE system. Timely reporting and digital monitoring could have prevented the loss.
Success Story: How Smart Warehousing Reduced Logistics Costs
A Tirupur-based apparel exporter faced recurring shipment delays due to scattered storage and transport coordination issues.
After partnering with a bonded warehouse near Chennai port and integrating their operations with Cargo People’s digital distribution network, they:
-
Cut logistics costs by 27% per shipment.
-
Reduced export cycle time from 9 days to 5 days.
-
Eliminated double-duty payments on re-exports.
This transformation showcases how strategic warehousing and distribution planning can boost international reliability and client satisfaction.
5 Key Takeaways for Indian Exporters & Importers
-
Use bonded or FTWZ facilities to defer duties and optimize capital flow.
-
Adopt tech-based warehouse management (WMS, ULIP tracking, ICEGATE reporting).
-
Locate near major ports like Nhava Sheva, Mundra, or Chennai to minimize inland transit.
-
Ensure WDRA, DGFT, and BIS compliance to avoid costly penalties.
-
Integrate distribution logistics to achieve visibility from warehouse to vessel.
FAQs
1. What is a bonded warehouse in India?
A bonded warehouse allows importers to store goods without paying customs duty until release, improving cash flow and compliance control.
2. What is the difference between FTWZ and bonded warehouse?
FTWZs fall under the SEZ Act and focus on international trade and re-exports, while bonded warehouses operate under the Customs Act for domestic imports.
3. How does warehousing help exporters save money?
It reduces demurrage, optimizes freight consolidation, and delays duty payment until actual sales or shipment.
4. What are the main warehousing compliance requirements in India?
Licensing under CBIC 2016/2024 rules, WDRA registration, and proper monthly returns via ICEGATE.
5. Which ports offer the best warehousing facilities?
Nhava Sheva, Mundra, and Chennai are top choices for bonded and FTWZ facilities due to connectivity and customs efficiency.
6. How can Cargo People support my warehousing needs?
By offering bonded storage, customs documentation, distribution logistics, and port coordination through our all-India network.
Conclusion — Turning Storage into Strategy
In modern trade, success is measured not just by how far goods travel but how efficiently they move through every checkpoint.
For Indian exporters and importers, a strategic warehousing and distribution setup isn’t just about space—it’s about saving time, avoiding penalties, and strengthening customer trust.
At Cargo People Logistics, we help businesses design cost-effective, compliant, and technology-driven warehousing solutions near India’s key trade hubs — including Delhi NCR, Mundra, Nhava Sheva, and Chennai.
📞 +91 78350 06245
📧 Cha@cargopeople.com
Book a Consultation with Cargo People Logistics

 USA
USA
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Germany
Germany
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Canada
Canada
 New Zealand
New Zealand