A manufacturer in Delhi ships a high-value consignment overseas. A portion gets returned due to a quality mismatch. As the shipment arrives back in India, confusion around documentation, incorrect HS codes, and customs queries begins piling up. Day by day, detention charges grow. The team realises the return journey is far more complex than the original export.
This sets the stage for how reverse logistics truly works and why the combined expertise of a CHA and a freight forwarder matters.
Why Reverse Logistics Matters for Indian Businesses Today
Introduce the rising volume of returns across sectors and how global buyers expect return mechanisms to be as smooth as forward shipping.
Explain how Indian exporters, importers, and manufacturers are seeing returns affect cash flow, inventory accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
Bullet themes:
-
India’s return volumes are increasing across e-commerce, apparel, electronics, industrial goods.
-
Reverse logistics is often the single largest hidden cost in international trade.
-
Poor planning leads to demurrage, duty disputes, and rework losses.
What Reverse Logistics Really Means for Cross-Border Trade
Define reverse logistics in the context of India’s export–import ecosystem.
Highlight how it is not just about taking goods back, but ensuring compliance and cost efficiency during the return journey.
Sub-themes:
-
Product returns due to defects or mismatches
-
Warranty or RMA shipments
-
Re-import after exhibitions or temporary exports
-
Unsold stock returning from overseas warehouses
-
End-of-life or recycling-based returns
The Challenges Most Businesses Overlook in Return Shipments
Show the silent risks that appear during return cargo movement, especially cross-border.
Bullet themes:
-
HS code mismatch leading to customs queries
-
Incorrect “reason for return” affecting duty exemption eligibility
-
Missing or mismatched documents between original export and return shipment
-
Port delays caused by lack of coordination between overseas shipper and Indian CHA
-
Storage, reworking, and detention fees accumulating faster than expected
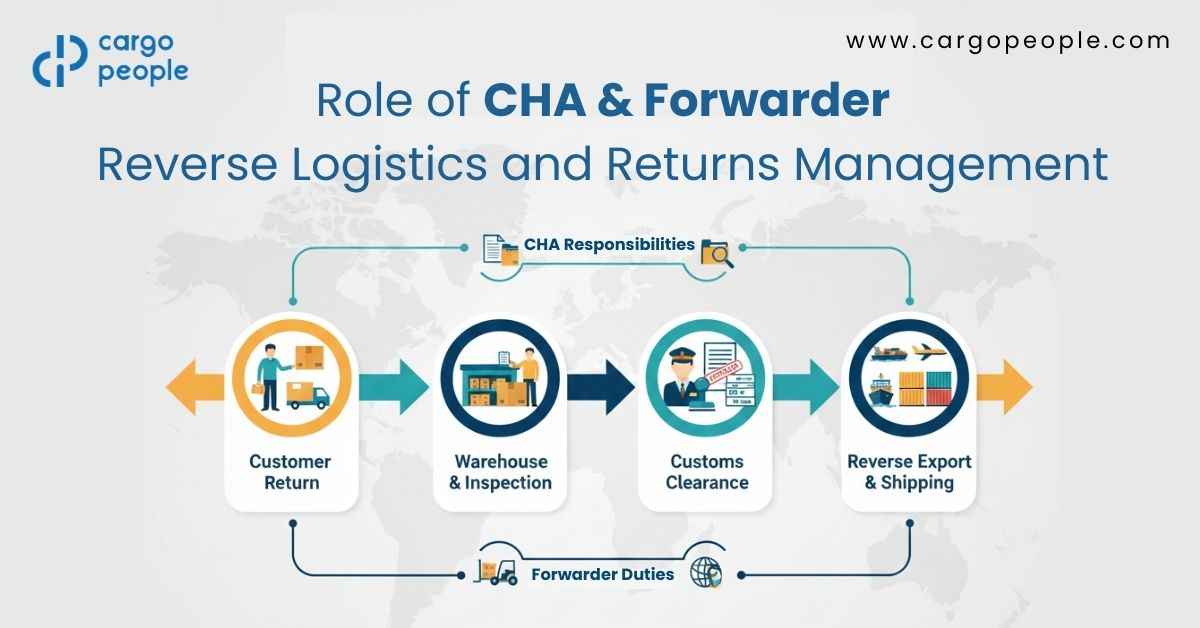
The Role of the CHA in Smooth and Compliant Reverse Logistics
Explain how the CHA becomes the central compliance expert during the re-import process.
Sub-themes:
Documentation and Compliance:
-
Preparing and filing the Bill of Entry for re-imports
-
Aligning HS codes with the original export documentation
-
Applying the correct exemptions or duty relief provisions
-
Handling customs queries and ensuring smooth clearance
High-Risk Scenarios Where a CHA Is Critical:
-
Temporary exports returning after repair or testing
-
Warranty replacements
-
Goods returned beyond standard time limits
-
Valuation disputes or missing paperwork
Risks Without an Experienced CHA:
-
Costly penalties
-
Multi-day delays at port
-
Incorrect duty assessment
-
Repeated documentation filing
The Freight Forwarder’s Role: Managing the Physical Return Journey
Describe how the forwarder handles the operational and cost side of reverse cargo movement.
Sub-themes:
-
Arranging pickup from buyers, distributors, or warehouses abroad
-
Choosing the most economical return route
-
Managing packing, labeling, and documentation at origin
-
Negotiating rates for low-volume return cargo
-
Consolidation strategies for multi-country returns
Cost and Speed Optimisation:
-
Mode selection (air, sea, courier, or combination)
-
Using bonded facilities to avoid upfront duty payments
-
Designing return windows for seasonal or bulk shipments
How CHA and Forwarder Work Together in an Integrated Reverse Logistics Model
Show the synergy between both roles and how it reduces touchpoints and errors.
Sub-themes:
Typical Workflow:
-
Buyer initiates a return
-
Forwarder coordinates pickup, packaging, and initial paperwork
-
CHA reviews documentation before cargo moves
-
Shipment arrives at port; CHA files re-import documents
-
Duty assessment and exemption application
-
Cargo moves to warehouse or customer location
Business Advantages:
-
Fewer documentation errors
-
Faster clearances and reduced storage charges
-
Better communication across customs, carriers, and warehouses
-
Significant savings on return freight and duties
Data Table: Customs Clearance Timelines in India (Forward vs Return)
| Process Type | Average Days at Major Indian Ports | Common Delay Points | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Export | 2–3 days | Documentation mismatch, scanning | Missed vessel cut-offs |
| Reverse Import (Returns) | 3–6 days | Valuation queries, HS code mismatch, exemption checks | Storage cost, delayed dispatch, duty disputes |
Interpretation:
Reverse flows require more scrutiny and documentation, making CHA involvement essential.
Data Table: Cost Comparison for Return Shipping Routes
| Mode | Average Cost per 100 kg | Transit Time | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Freight | ₹35,000–₹55,000 | 2–5 days | Warranty returns, urgent shipments |
| LCL Sea Freight | ₹8,000–₹15,000 | 15–35 days | Bulk retail returns, rejected orders |
| Express Courier | ₹12,000–₹25,000 | 3–7 days | High-value small parts and samples |
Interpretation:
Cost-effective returns depend on selecting the right mode; a forwarder ensures this decision aligns with urgency and cargo value.
Conclusion: Why Indian Businesses Need a Structured Reverse Logistics Strategy
Reverse logistics is no longer a background function. It affects customer trust, cash flow, inventory health, and compliance exposure.
A CHA ensures documents, duties, and customs processes are accurate.
A freight forwarder ensures movement is efficient, economical, and predictable.
Together, they give Indian businesses the clarity and control needed to handle returns without disruption.
CTA:
📧 Cha@cargopeople.com
Book a consultation with Cargo People Logistics

 USA
USA
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 Germany
Germany
 Argentina
Argentina
 Australia
Australia
 Canada
Canada
 New Zealand
New Zealand